Pneumatic Tourniquet System
Automatic pneumatic tourniquet system is a professional equipment used in medical surgery, mainly through the air pump to press the gas into the pressure cuff, generating uniform pressure effect on the blood vessels of the limbs, controlling the local blood flow, and realizing the bloodless operation environment during the operation.
Compared with traditional manual hemostatic devices, it has the advantages of easy operation, precise pressure and high safety.
Key Applications of Pneumatic Tourniquet System
Orthopaedic Surgery
•Extremity Procedures: Used in surgeries like fracture repositioning, joint replacements (e.g., knee, hip), and internal fixation to minimize bleeding and provide a clear surgical field. •Amputations:Effectively controls bleeding during amputation surgeries, aiding surgical efficiency. •Limb Deformity Corrections: Ensures a bloodless environment for successful limb deformity surgeries.
Plastic surgery
•Flap Transplantation:Helps minimize bleeding during skin flap transplantation or repair, ensuring a clear view for surgeons. •Limb Reconstruction:Assists in scar repair and deformity corrections on limbs.
Hand Surgery
•Fine Hand Surgeries: Used in tendon and nerve repair, and reimplantation of severed fingers to provide a bloodless operating environment for precise procedures. •Trauma Repair:Essential for controlling bleeding during hand trauma surgeries, stabilizing the patient for further interventions.
Vascular Surgery
•Repair & Reconstruction:Temporary blockage of blood flow during vascular repairs or transplants enables safer surgical interventions. •Circulation Testing:Used for the tourniquet test to assess blood circulation in limbs.
Sports Medicine
•Arthroscopic Procedures:In knee and shoulder arthroscopy, it reduces intra-articular bleeding, improving the clarity of the surgical field. •Injury Repair:Facilitates ligament and cartilage repairs, enhancing surgical outcomes.
Trauma Surgery
•Acute Trauma:Provides temporary hemorrhage control in severe limb trauma (e.g., car accidents), stabilizing the patient before surgery. •Open Fracture Repair:Reduces bleeding during open fracture surgeries, ensuring optimal conditions for surgical repair.
Paediatrics
•Pediatric Limb Surgeries:The pneumatic system adjusts pressure for the unique needs of children’s limbs, ensuring safety and effectiveness during orthopaedic or hand surgeries. •Congenital Deformity Surgery:Aids in correcting congenital limb deformities with minimal bleeding.
Rehabilitation
•Ischemic Training:In rehabilitation, the tourniquet system is used for ischemic training, which promotes muscle recovery and enhances function by briefly restricting blood flow.
Emergency or Field medicine
•Temporary Haemostasis:Used in emergency settings to control severe bleeding from limb injuries, buying critical time for transport or further surgery. •Battlefield First Aid:In disaster zones or on battlefields, the pneumatic tourniquet serves as a life-saving tool for controlling hemorrhage
Our Product Selection
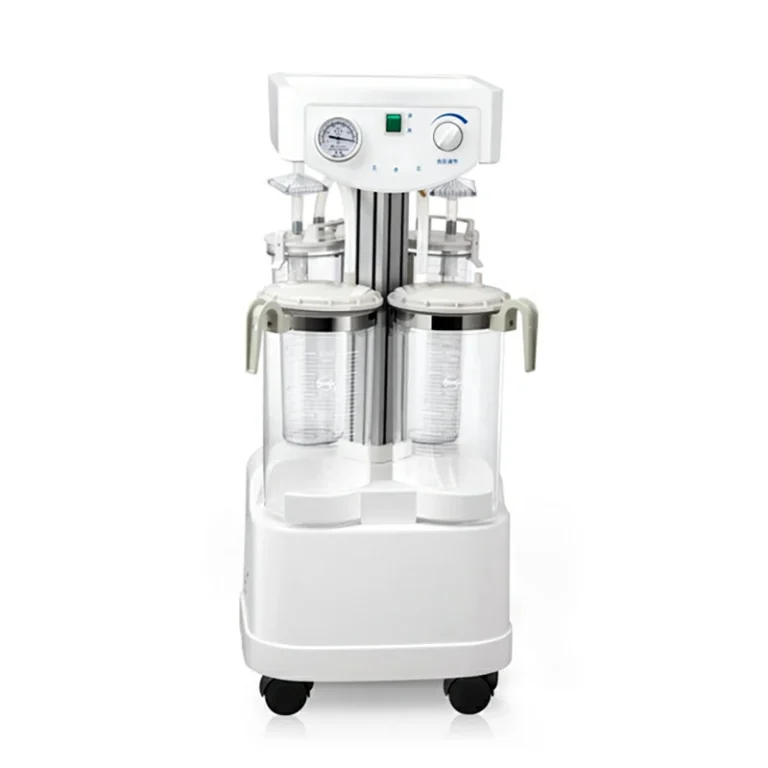

CNME-PT1A
Automatic Tourniquet System
Single Channel
Button screen
Maximum setting pressure:650mmHg
Maximum working time :1-100min
Pressure adjustment accuracy: +25mmHg
Built-in Lithium-ion battery
Working noise :≤80dB
Standard with 3 TPU cuffs & trolley
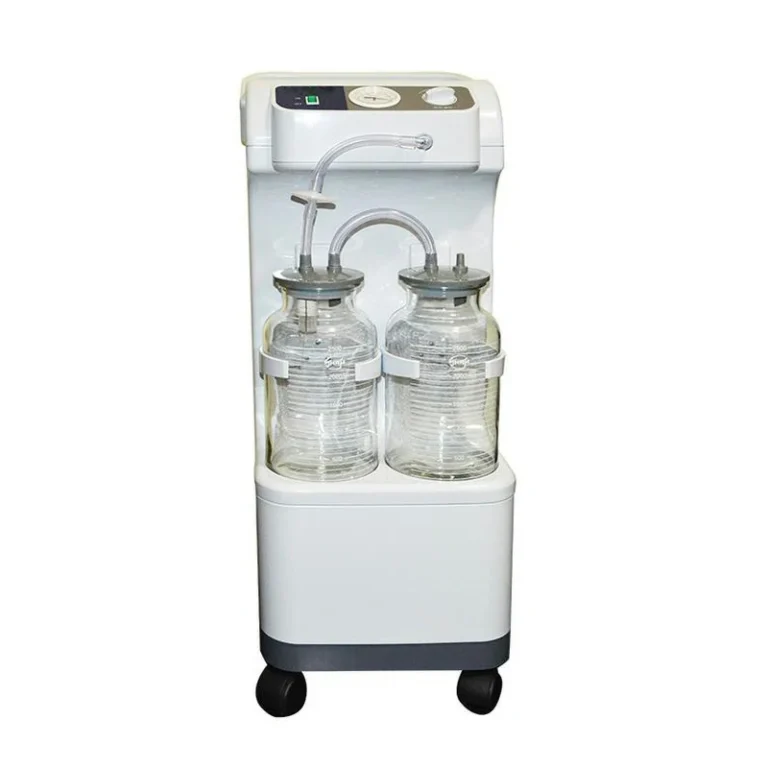

CNME-PT1B
Automatic Tourniquet System
Double Channel
Button screen
Maximum setting pressure:650mmHg
Maximum working time :1-240min
Pressure adjustment accuracy: +25mmHg
Built-in Lithium-ion battery
Working noise :≤80dB
Standard with 6 TPU cuffs & trolley
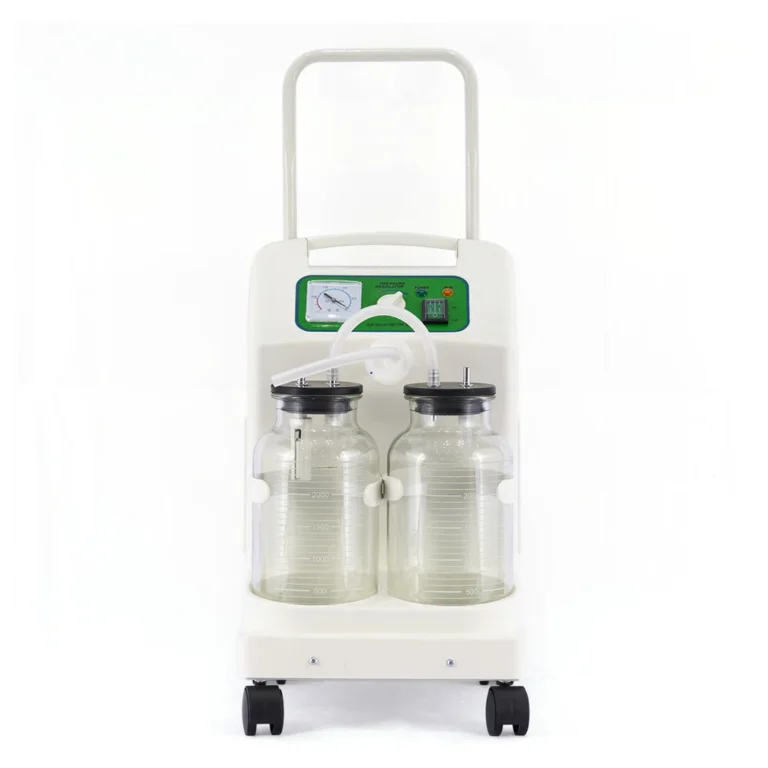

CNME-PT2B
Automatic Tourniquet System
Double Channel
Touch screen
One-click conversion between mmHg & kPa
Maximum setting pressure:650mmHg
Maximum working time :1-240min
Built-in Lithium-ion battery
Working noise :≤60dB
Standard with 6 TUP cuffs & trolley

Components of automatic pneumatic tourniquet
1. Control Host: the core part of the equipment, responsible for regulating the pressure, control time and monitor the operating status of the equipment.
Main Components:
Display, control panel, built-in pump system, safety alarm system
2. Pressure Cuff: a component in direct contact with the patient’s extremity used to apply uniform mechanical pressure to block local blood flow.
3. Connection Line: connects the main unit to the pressure cuff to transmit air pressure.
4. Power supply system: Provide the power support required for the operation of the equipment to ensure a long period of continuous work.
5. Accessories And Consumables
Common Accessories: replacement cuffs, cleaning kits, protective caps for line connections
Consumables: Cuffs and connecting tubes may need to be replaced periodically to ensure hygiene and reliable performance.
Guidelines for Using the Pneumatic Tourniquet System

Indications and Contraindications
Pressure Setting
Duration of Use
Tourniquet Placement
Postoperative Care

