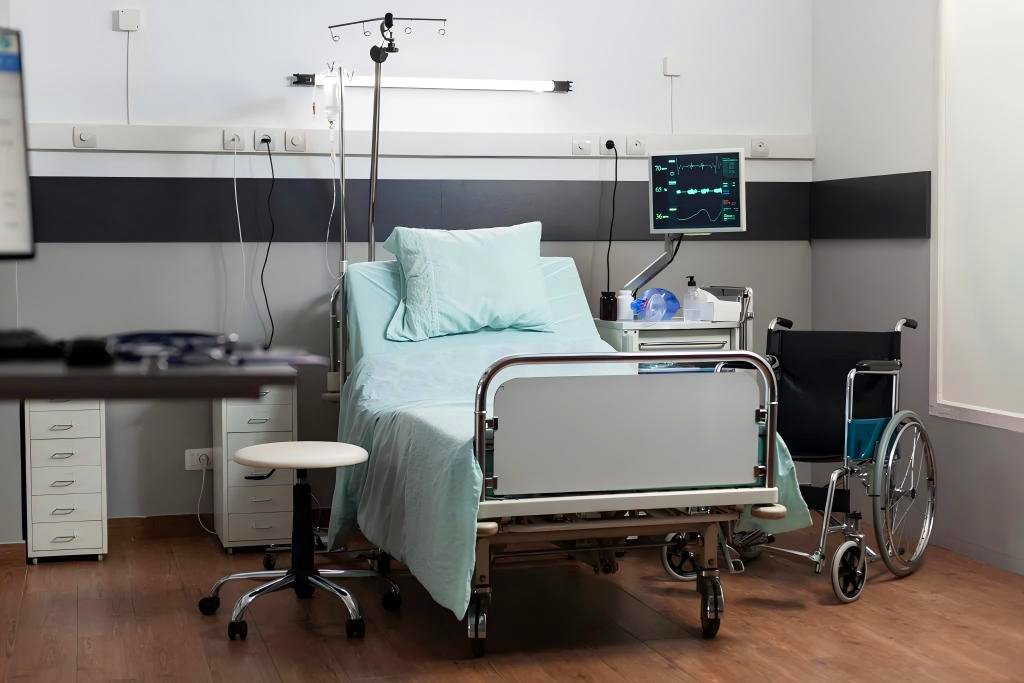
Understanding Hospital Furniture and Rehabilitation Equipment
Hospital Furniture
Hospital furniture supports diagnostic and treatment processes and ensures environmental safety. It spans a wide range of facility types across reception, waiting, diagnosis, care, inpatient, and office areas. Design priorities include cleanability, durability, and infection control, with materials commonly being corrosion-resistant. It must strictly meet zoning requirements for clean/contaminated areas and accessibility standards.
Rehabilitation Equipment
Rehabilitation equipment refers to medical-specific devices aimed at improving function and compensating for impairments. It includes four core functional categories: assessment, training, physical therapy, and assistance, such as muscle strength training devices and cognitive tools. Equipment use must be guided by medical staff to ensure training efficacy. Most must meet medical device safety access standards.
Significance of Hospital Furniture & Rehabilitation Equipment
Enhancing Safety for Medical Staff
Properly designed furniture and well-operated equipment significantly reduce the risk of occupational injury. Anti-slip and stable structural designs prevent accidents during handling or operation. Corrosion-resistant and easy-to-clean features minimize cross-contamination risks, establishing a solid safety barrier in medical settings.
Meeting the Comfort Needs of Patients’ Families
Furniture in waiting and accompanying areas directly affects the physical and emotional experience of family members. Ergonomic seating and convenient facilities ease the fatigue of prolonged waiting. A calm and tidy space helps reduce anxiety and conveys warmth and humane care.
Supporting Patients’ Rapid Recovery
Targeted equipment addresses specific dysfunctions for efficient rehabilitation. Functional beds and assistive devices help maintain proper posture, prevent complications, and reduce bed rest duration. Scientifically integrating therapy environments with rehab tools creates optimal physical and psychological conditions for functional recovery.
Checklist of Hospital Furniture & Rehabilitation Equipment
1. Medical Furniture
Bed Types:
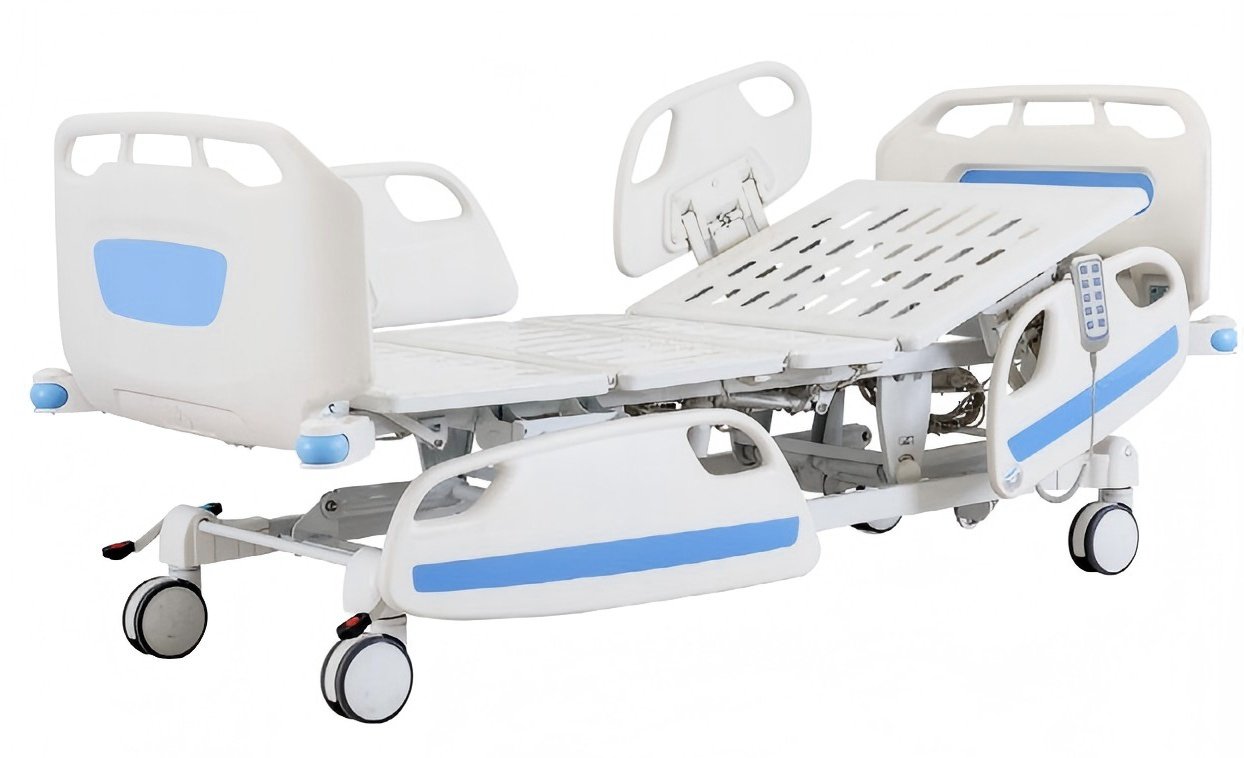
- Hospital Bed:Core facility in inpatient wards, supporting patients’ rest, sleep, and basic care operations, often equipped with safety rails for added protection.
- Nursing Bed:A professional bed with multi-position angle and height adjustments, significantly improving ergonomic experience and work efficiency for routine care, bathing, and treatment.
- Baby Crib:Specifically designed for newborns and infants, featuring safety rails and a soft interior, providing a cozy and protective space for sleeping and observation.
- Examination Bed: Found in clinics and outpatient treatment rooms, offering a stable surface for physical exams, dressing wounds, and simple care procedures.

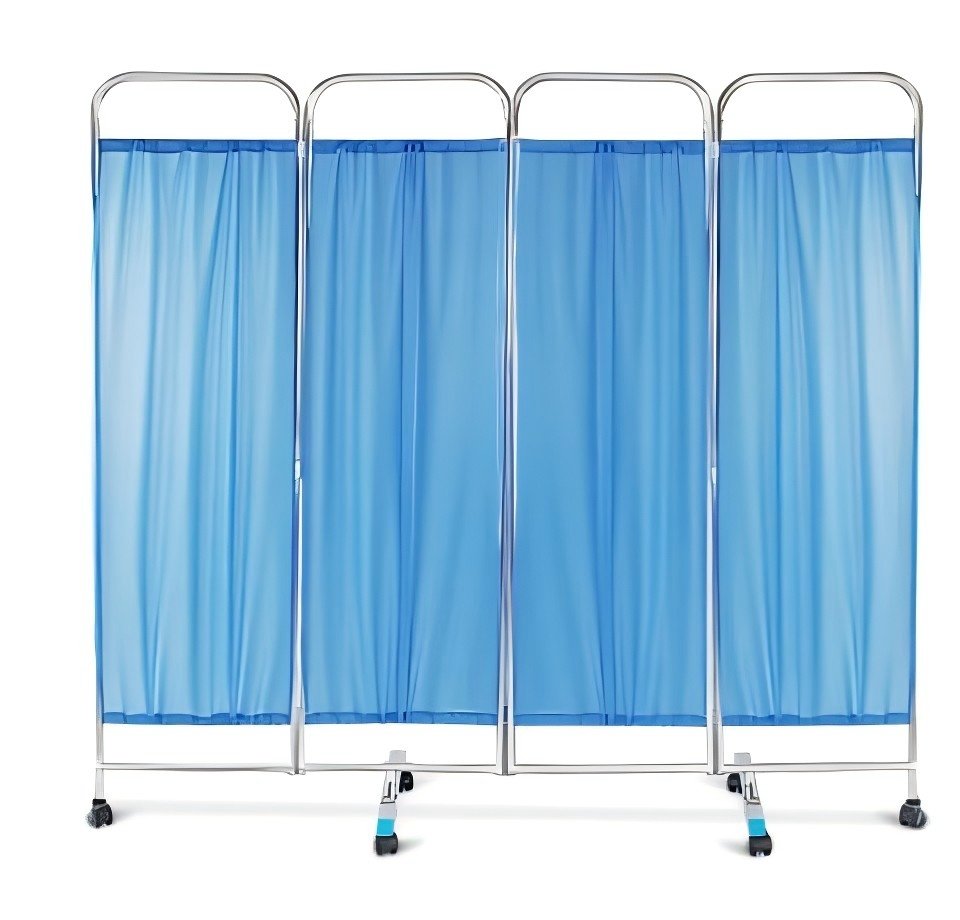
Medical Screen: A mobile partition used to create private spaces instantly in busy medical settings, protecting patient privacy during treatment, dressing, or personal care.

IV Pole: A basic stand for suspending IV bags, blood bags, or infusion pumps, essential for ensuring safe and uninterrupted intravenous therapy.

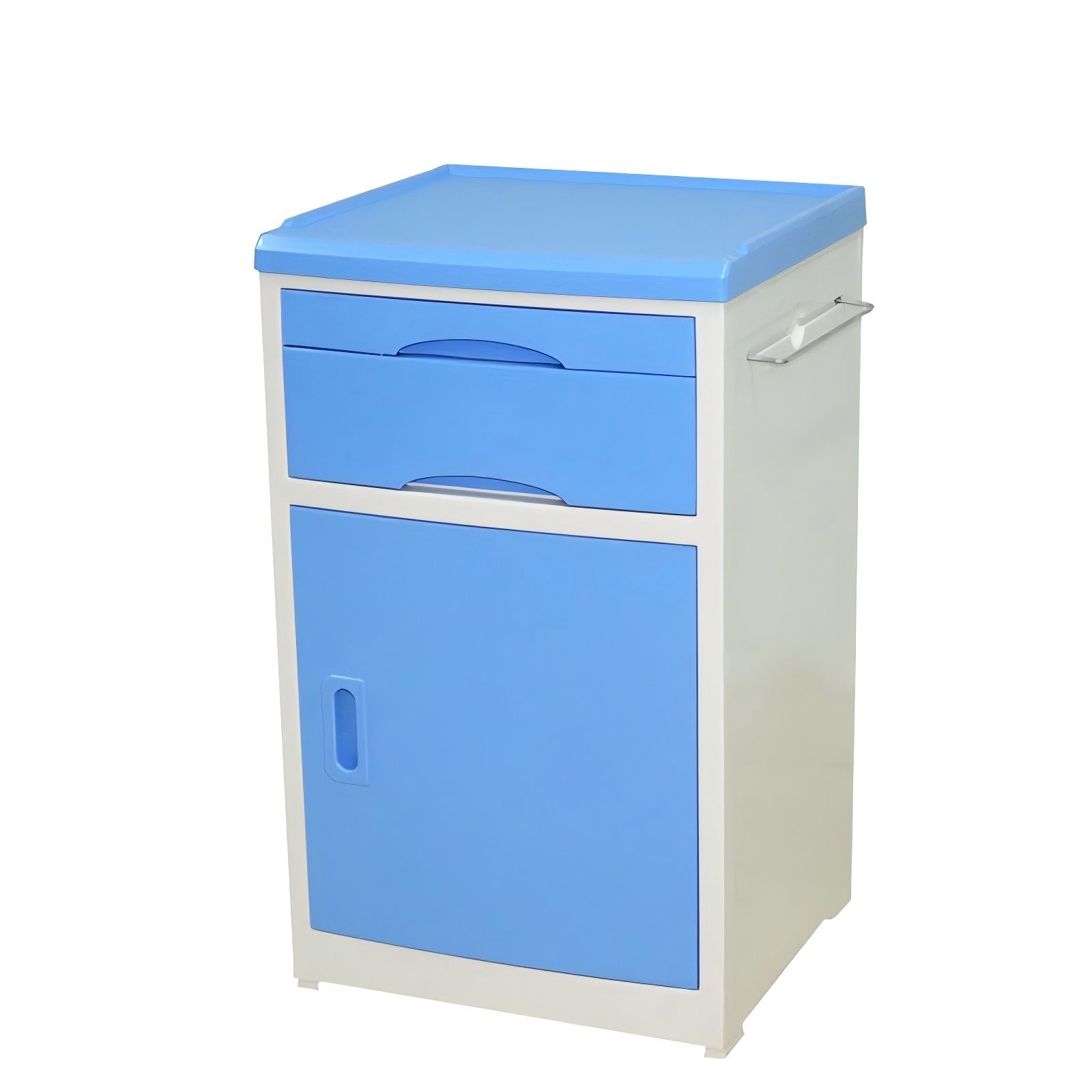
Bedside Cabinet: A small personal storage unit next to the bed, enabling patients to access water, medications, tissues, and personal items conveniently.
Bedside Table: A movable table often integrated with the hospital bed, facilitating dining, reading, writing, or temporary storage while bedridden.

Infusion Chair: Specialized seating for outpatient IV rooms or day treatment areas, equipped with a sturdy, adjustable IV pole to ensure comfort during extended infusions.
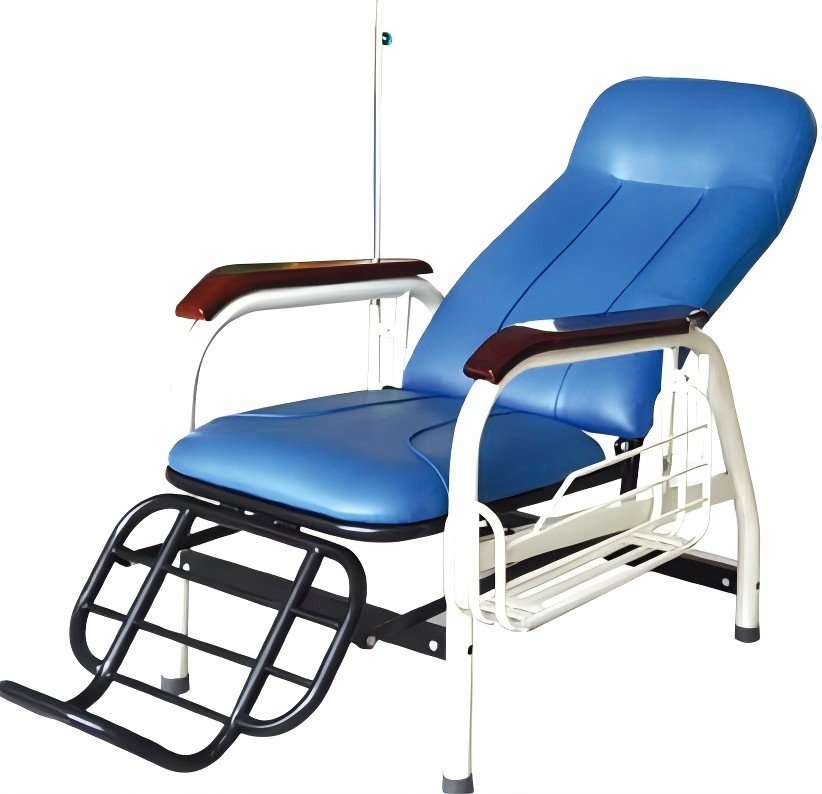
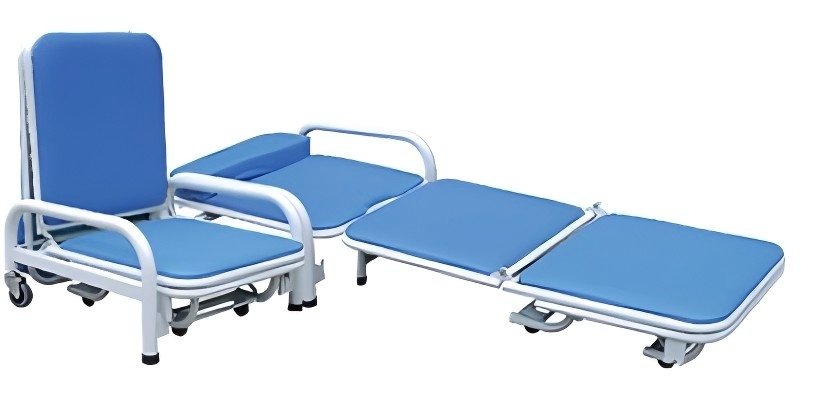
Escort Chair: Space-saving, foldable chairs for caregivers, offering dignified rest options for family members accompanying inpatients.
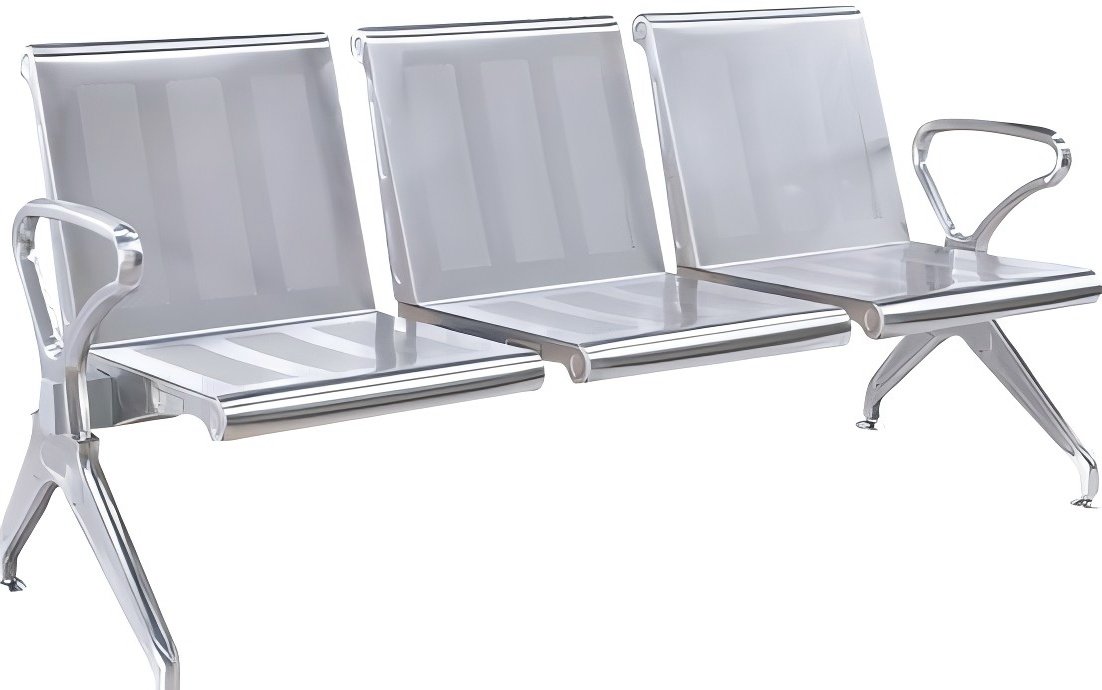
Waiting Chair: Row or single chairs placed in outpatient lobbies and waiting areas, meeting the basic seating needs of large volumes of patients and companions.

Medical Stool: Designed for frequent movement and close-range tasks, lightweight and easily cleaned, supporting tasks like IV preparation or bedside treatments.

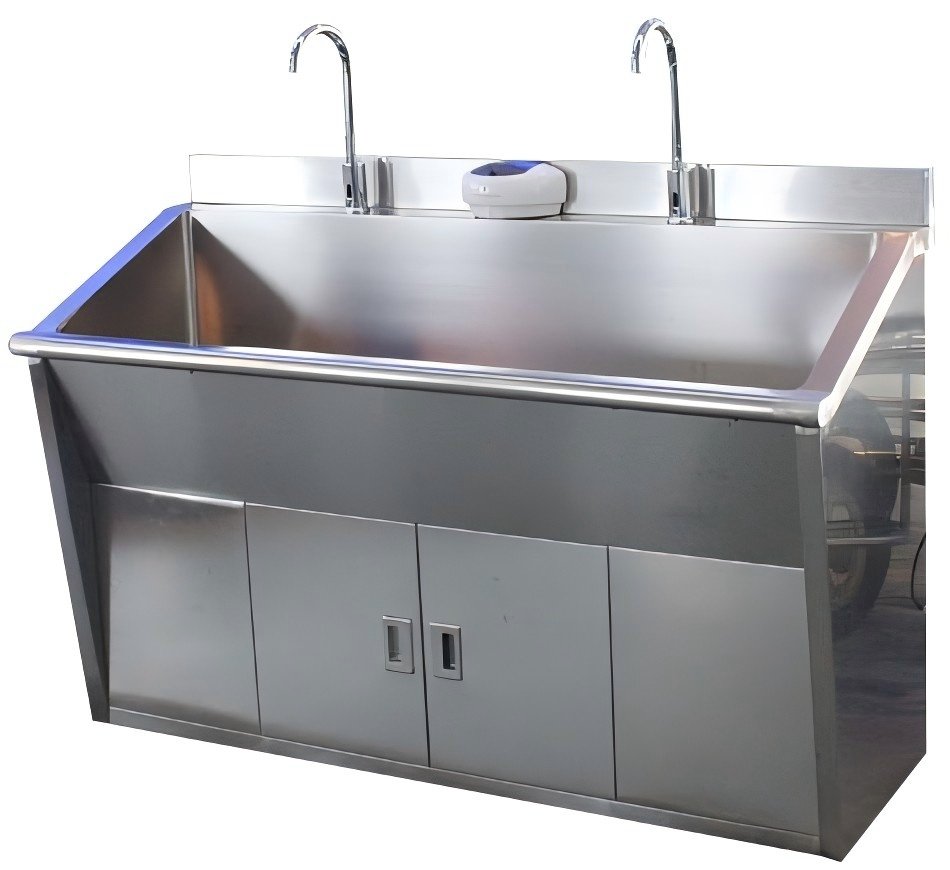
Hand-Washing Sink: Designed for high-frequency hand hygiene operations by medical staff, with sensor faucets and disinfecting facilities, fundamental for sterile workflows.

Trolley Types:
- Medical Trolley: Multipurpose trolley with tiered structure, enabling efficient transport of medications, emergency supplies, instruments, and documents across hospital units.
- Patient Trolley: Lightweight platform with shock absorption for safely moving temporarily immobile patients to departments like radiology.
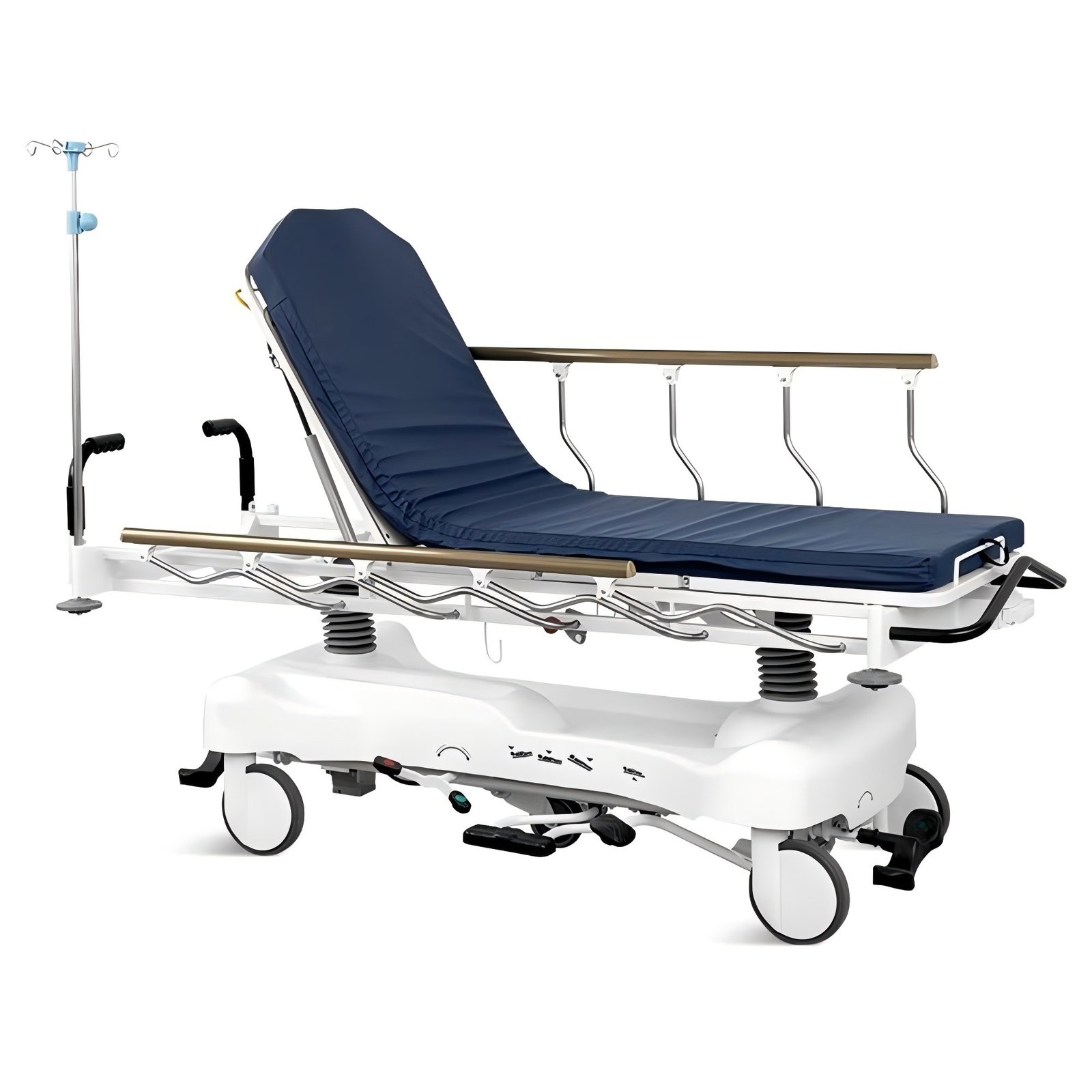
- Stretcher Trolley:Wheeled chassis tailored for emergency and stretcher use, ensuring safe transitions between bed, ambulance, and diagnostic platforms.
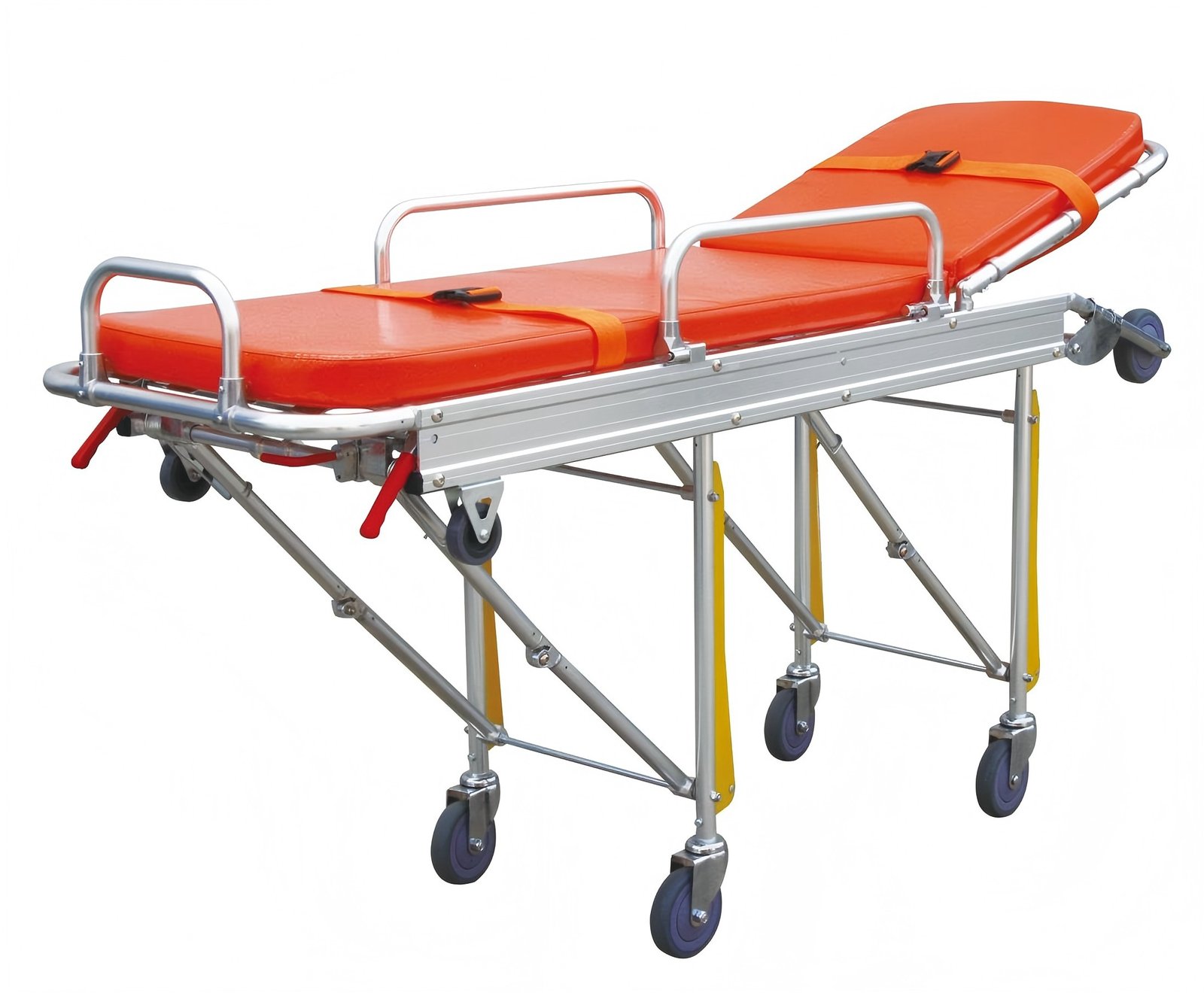
- Transfer Trolley: A base unit for moving heavy equipment (e.g., ventilators, monitors) or large items (e.g., linens) within the hospital efficiently.
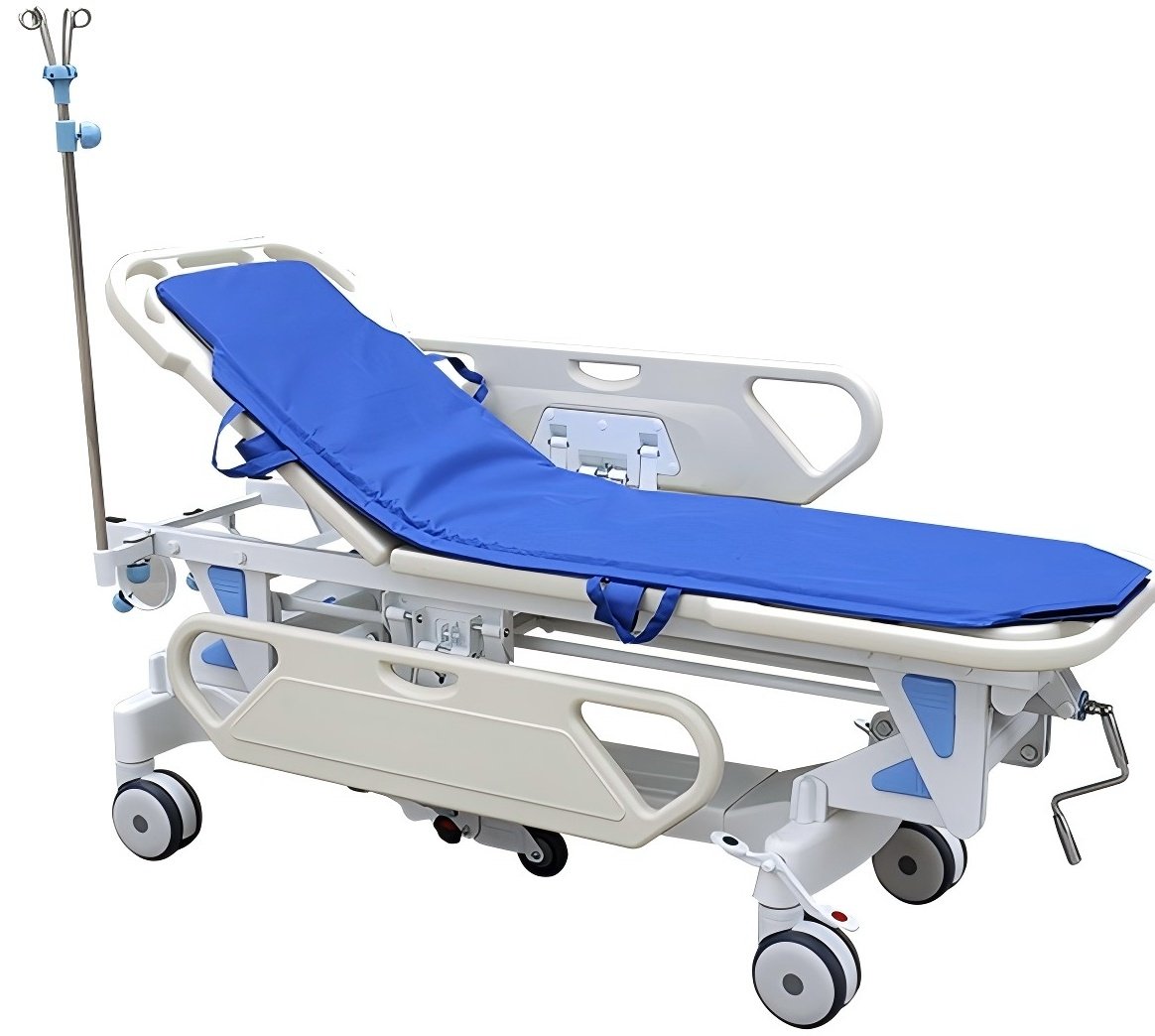
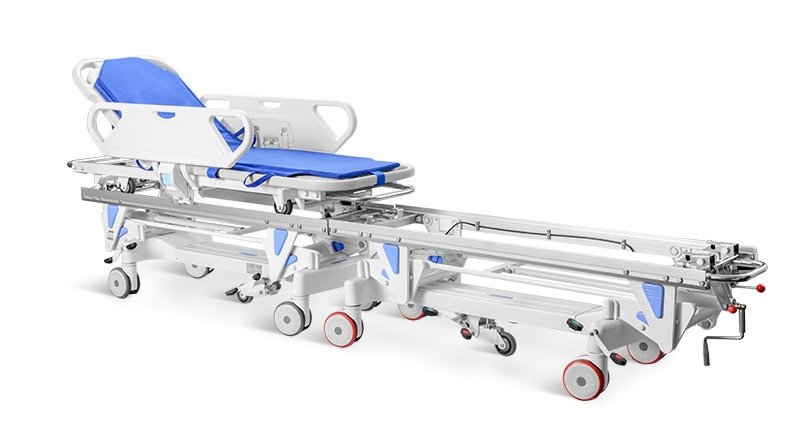
- Surgical Exchange Cart:A specially locked platform enabling seamless and secure patient transfer from hospital bed to surgical table.

Stretcher: A core tool in pre-hospital care and disaster rescue, used to support and transfer patients over long distances or through narrow spaces.
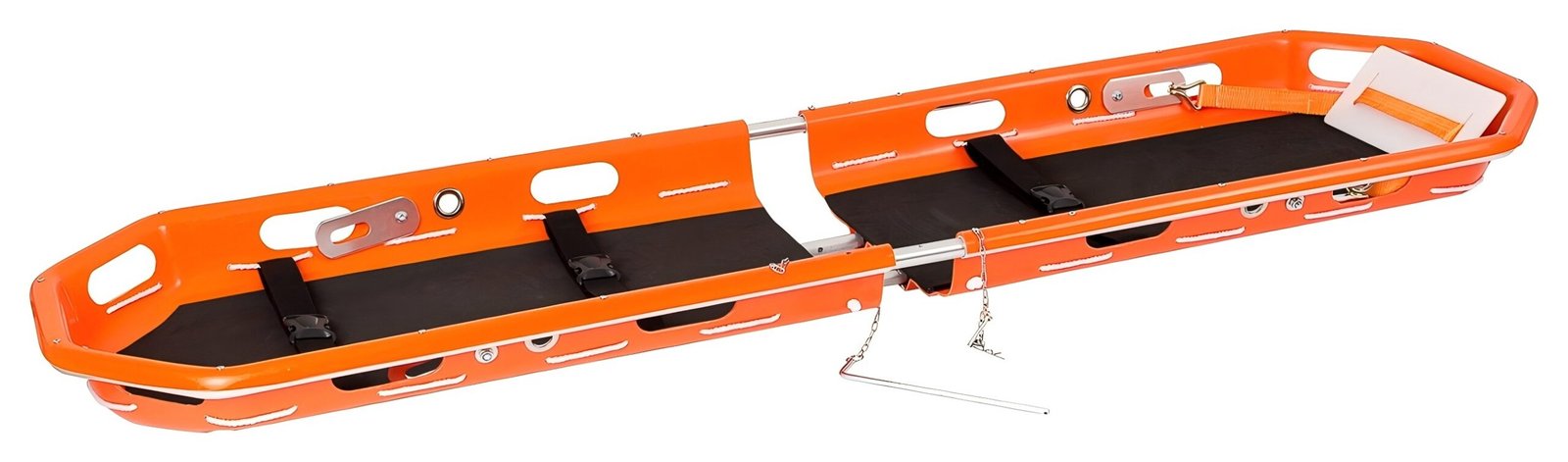

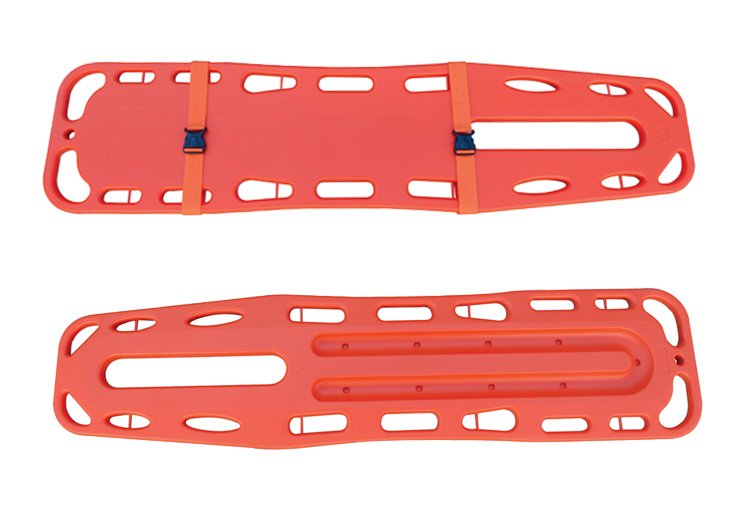
Spine Board: A rigid board contoured to the spine, used for emergency spinal immobilization on-site to minimize secondary injury during transport.
Corpse Cart & Dissection Table: System equipment used for temporary placement, refrigerated storage, organized transfer, and, when needed, forensic or pathological examination of deceased bodies.

2. Office Furniture
File & Instrument Cabinets: Dual-purpose units for archiving medical records and organizing instruments, offering categorized, clean, and contamination-controlled storage.

Medicine Cabinet: Designed for light- and temperature-sensitive drug storage, facilitating small-scale medication management and safety in clinics or wards.

Stainless Steel Workbench: Commonly used in pharmacies and sterile packing areas, offering durable, corrosion-resistant, and fully disinfectable surfaces for hygienic operations.

Office Desk: Workstations for medical teams to write medical records, operate computer systems, conduct discussions, and handle administrative tasks.

Office Chair: Ergonomically designed for prolonged desk work, providing effective support to reduce fatigue and maintain posture and concentration.

3. Rehabilitation Equipment
Wheelchair: A vital mobility aid for individuals with impaired movement, promoting independence, social participation, and partial self-care.

Walker: A wider, more stable support device than canes or crutches, helping patients with weak lower limbs or poor balance gradually regain walking confidence.

Crutch: Key support for individuals recovering from lower-limb surgery, degenerative diseases, or temporary instability, reducing load-bearing stress and preventing falls.

Cane: A basic mobility aid for those with minor leg discomfort or unsteadiness, enhancing stability during walking with lightweight support.

Toilet Chair: A hybrid seat and toilet designed for patients with difficulty transferring or standing for extended periods, ensuring safe and dignified toileting.

Bath Chair: A non-slip seat adapted to wet environments, allowing patients with weak legs or poor standing endurance to bathe safely and comfortably.

Key Factors in Choosing Hospital Furniture & Rehabilitation Equipment
Safety
Priority is absolute safety for both users and operators, eliminating all injury risks. Stability, non-toxic materials, and anti-slip and impact protection are essential—especially for vulnerable patients and frequent users.
Ease of Cleaning
Surfaces must be smooth, seamless, chemical-resistant, and quick-drying for high-frequency disinfection. Designs must eliminate dirt traps to cut off infection pathways.
Ease of Maintenance
Maintenance pathways must be optimized. Products should feature simple structures and easy-to-replace parts to reduce downtime, extend service life, and lower long-term costs.
Flexibility
Equipment should meet diverse needs: adjustable height and angles, modular expandability, adaptability to different body types and workflows, and room for future space reconfiguration.
Durability
Made of impact-resistant materials with robust construction to withstand frequent use and disinfection. Long life cycles reduce replacement costs and enhance long-term investment value.
Ergonomics
Design must address the needs of both caregivers and patients: easing staff strain during operations and providing comfort and convenience to support patient rehabilitation engagement.
Aesthetics
Soft colors and harmonious design alleviate patient stress and foster a healing atmosphere. Visual order also reinforces professionalism and human-centered care.
Total Cost
Go beyond upfront pricing to evaluate lifecycle costs, including ease of maintenance, spare parts, service life, and operational efficiency—for optimal capital allocation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most essential hospital furniture item?
The hospital bed is fundamental. It supports daily patient care and treatment while integrating essential features such as safety rails and positioning adjustments—directly impacting care efficiency and patient safety.
Why is rehabilitation equipment critical to recovery?
Rehabilitation equipment bridges the path to independent living. Through scientific support and progressive training, it helps patients regain basic functions like movement and walking, shortens recovery time, and reduces long-term care needs.
What are key factors in choosing a supplier?
—Product Range: A complete, medically compliant catalog that covers varied hospital scenarios in a one-stop solution, minimizing coordination complexity.
—Customization Ability: Ability to adapt sizes, functions, or clinical solutions based on medical needs.
—Quality Assurance: Certified by medical industry standards, with traceable QA systems and proactive maintenance and risk prevention.
—Delivery & Installation: Capable of damage-free transport for precision equipment and large furniture, with professional installation and on-site usage training.