What is Medical Laboratory Equipment?
Medical lab equipment refer to a collection of specialized tools, instruments, and apparatuses used in medical research and diagnostic activities. They are primarily used for processing and analyzing experimental samples to obtain medically relevant data. These devices assist professionals in conducting tests and generating results. Their core function is to provide objective evidence for disease diagnosis, health assessment, and medical research.
Importance of Medical Laboratory Devices
- Precision and Accuracy:They provide highly reliable analytical results, minimizing human error, laying a scientific foundation for disease diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and health assessment, and ensuring that medical decisions are based on rigorous objective data.
- Improved Efficiency: Automated workflows significantly accelerate sample processing, analysis, and reporting cycles to meet high testing demands, optimize laboratory resource allocation, shorten patient wait times, and improve overall diagnostic and treatment efficiency.
- Safety: Built-in protective designs, enclosed systems, and automated operations effectively isolate operators from infectious pathogens, toxic or hazardous samples, or reagents, reducing occupational exposure risks and ensuring a safe and stable laboratory environment.
- Data Collection and Analysis:The devices generate standardized, traceable, and massive testing data, which can be integrated into LIS (Laboratory Information System) for digital management, providing powerful information support for clinical decisions, epidemiological research, and disease trend analysis.
- Multifunctionality: Through modular design or integration of multiple technology platforms, they can flexibly meet diverse testing needs across key medical fields such as basic research, precision medicine, and public health.
Medical Laboratory Equipment List
Basic Medical Lab Equipment
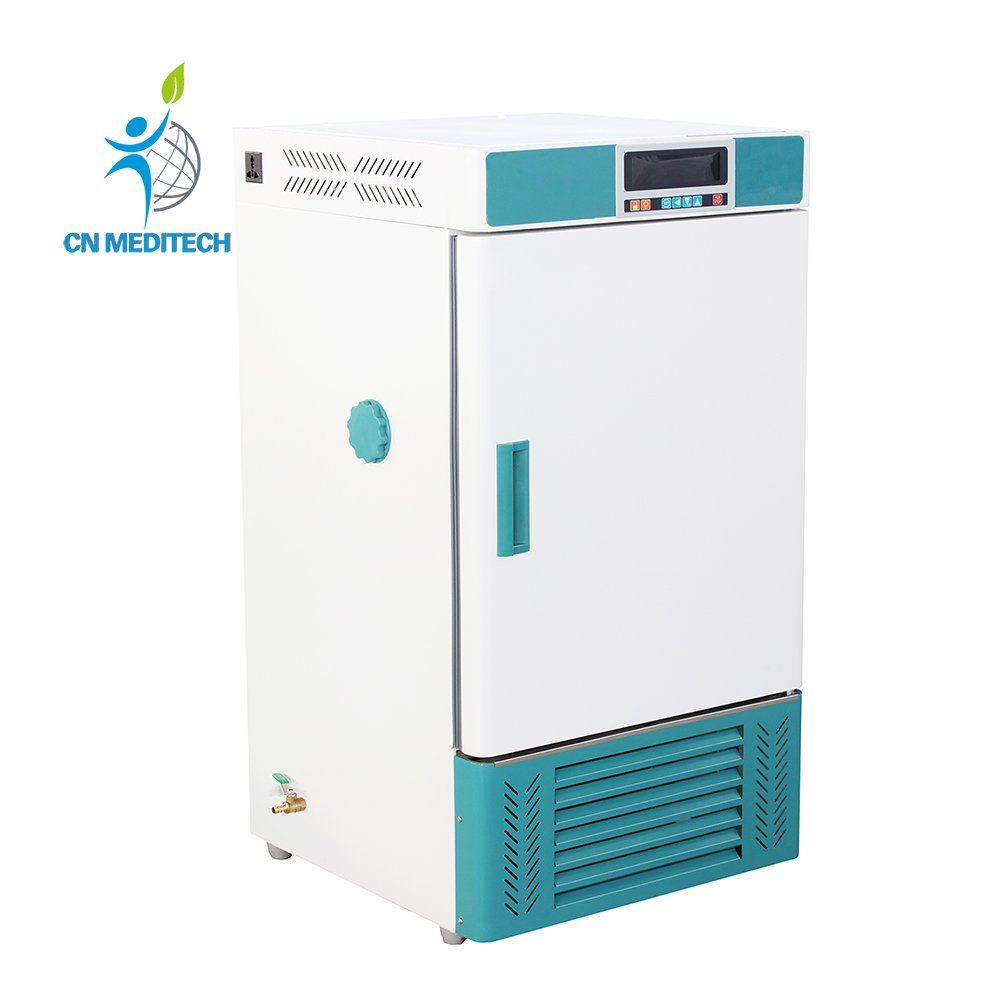
- Lab Incubator: Precisely controls temperature, humidity, CO₂ concentration, and light conditions to simulate specific microenvironments for the growth of cells, tissues, and microorganisms.
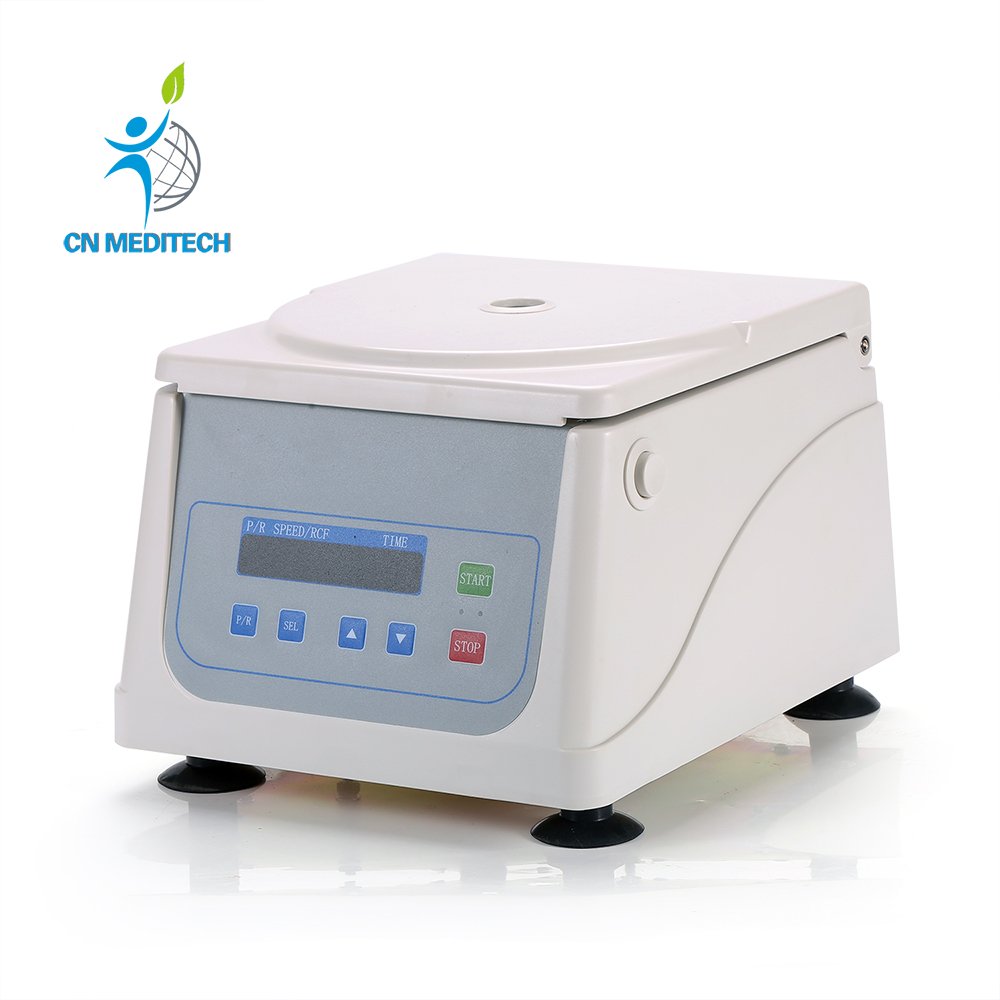
- Centrifuge: Uses high-speed rotation to generate centrifugal force, enabling efficient separation of sample components based on differences in density, size, or shape. Commonly used to separate serum or plasma from whole blood, precipitate cells or microorganisms, concentrate proteins or nucleic acids, and isolate cellular fractions.
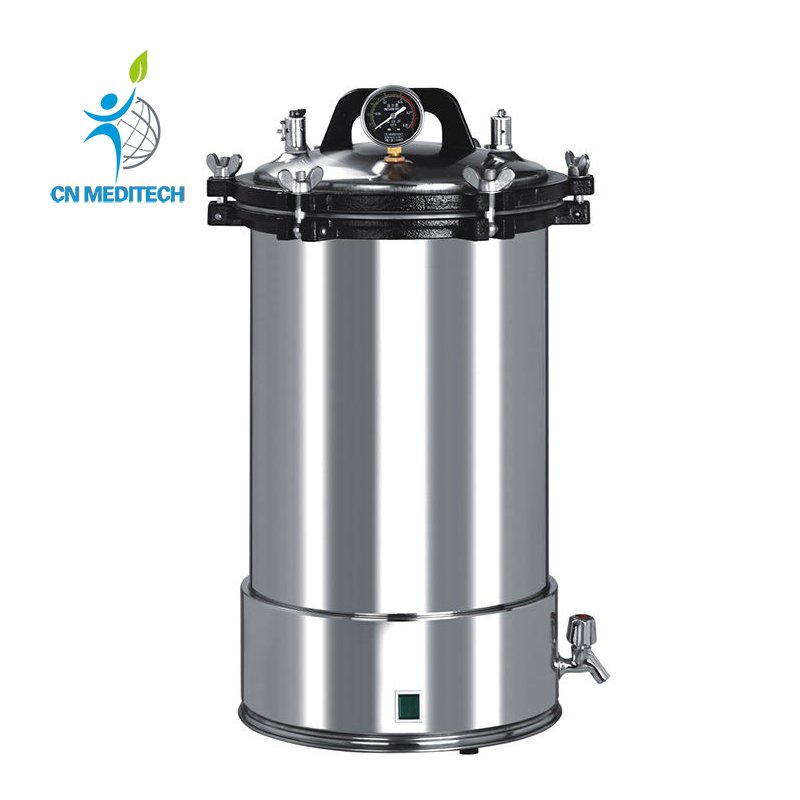
- Sterilizer:Utilizes high-pressure saturated steam (pressure sterilizer) or dry heat to thoroughly inactivate microorganisms in medical waste, lab instruments, culture media, and reagents under set temperature and pressure, achieving medical-grade disinfection and sterilization.
- Medical Freezer& Cooler: Provide stable storage environments in various temperature zones (refrigeration ~2–8°C, freezing ~–20°C to ultra-low –80°C) for temperature-sensitive chemical reagents, enzymes, standards, media, biological samples, and diagnostic kits to maintain stability and activity.
- Laminar Flow Cabinet: Uses high-efficiency filters to deliver continuous, unidirectional, high-purity airflow to create a localized sterile environment, protecting core experimental procedures from dust and particle contamination.
- Biological Safety Cabinet: Provides a physical barrier and directional airflow to ensure triple protection for personnel, samples, and the environment—an essential safety barrier in biohazard operations.
- Flow Clean Bench:Offers a localized dust-free, contamination-free space for object protection without direct biological protection for personnel—suitable for precision procedures requiring a clean environment.
Small Laboratory Equipment
- Pipette:Manual or electronic precision liquid handling tool for accurate aspiration, transfer, and dispensing of micro-volumes of liquid samples or reagents.
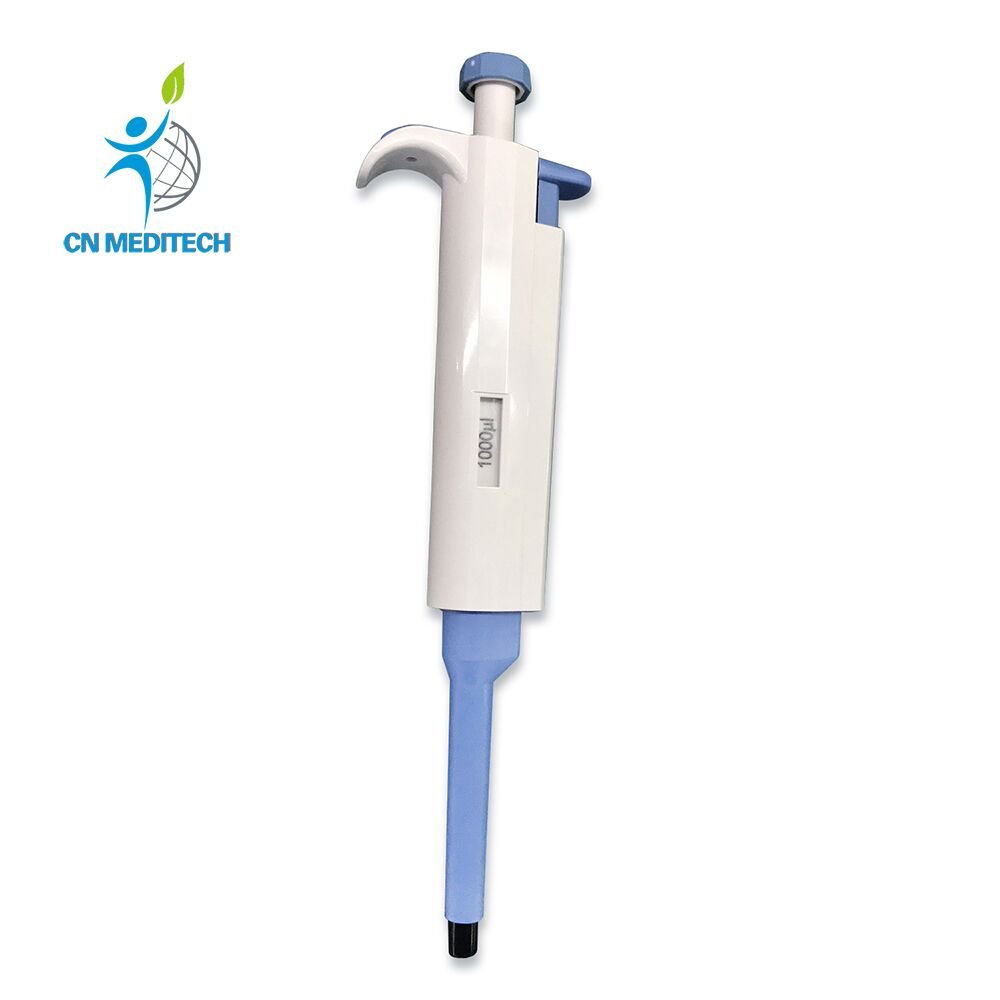
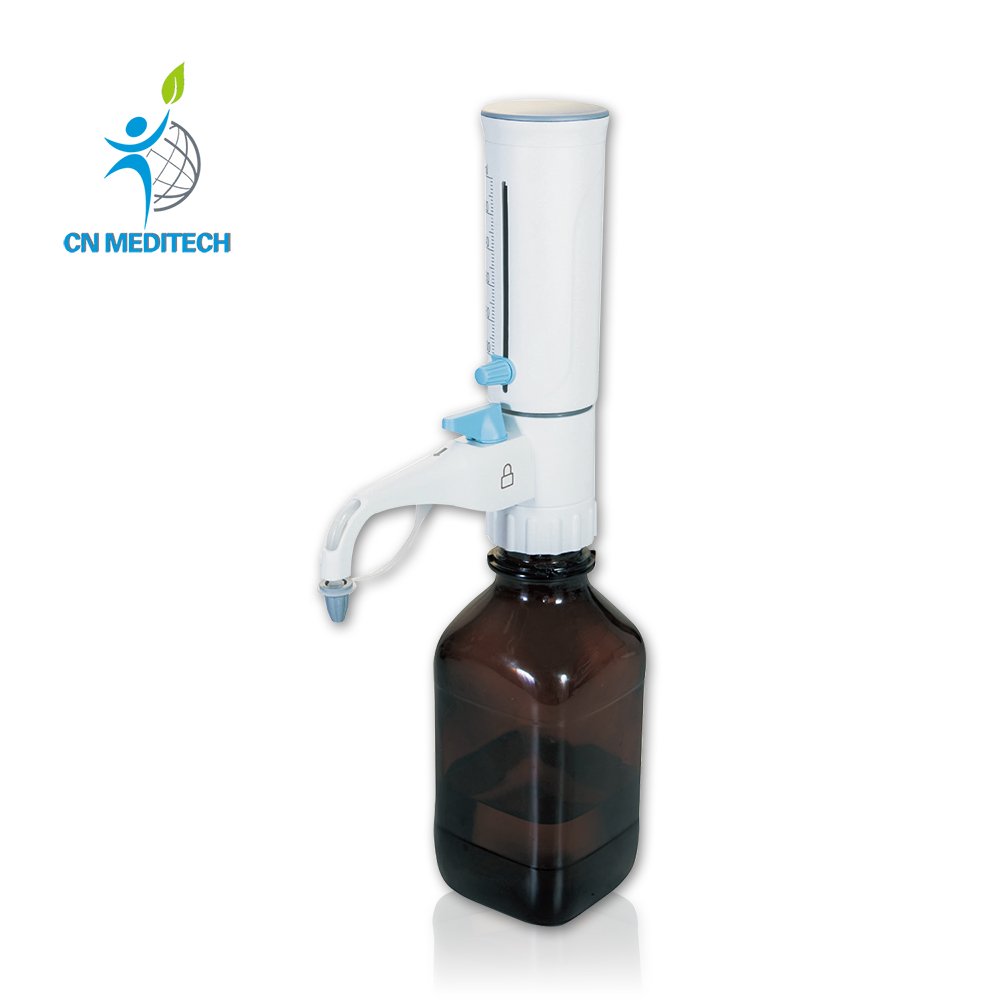
- Dispenser: Quickly dispenses fixed volumes of common liquids, enhancing workflow efficiency and reducing manual repetitive operations—commonly used for reagent preparation or media replenishment.

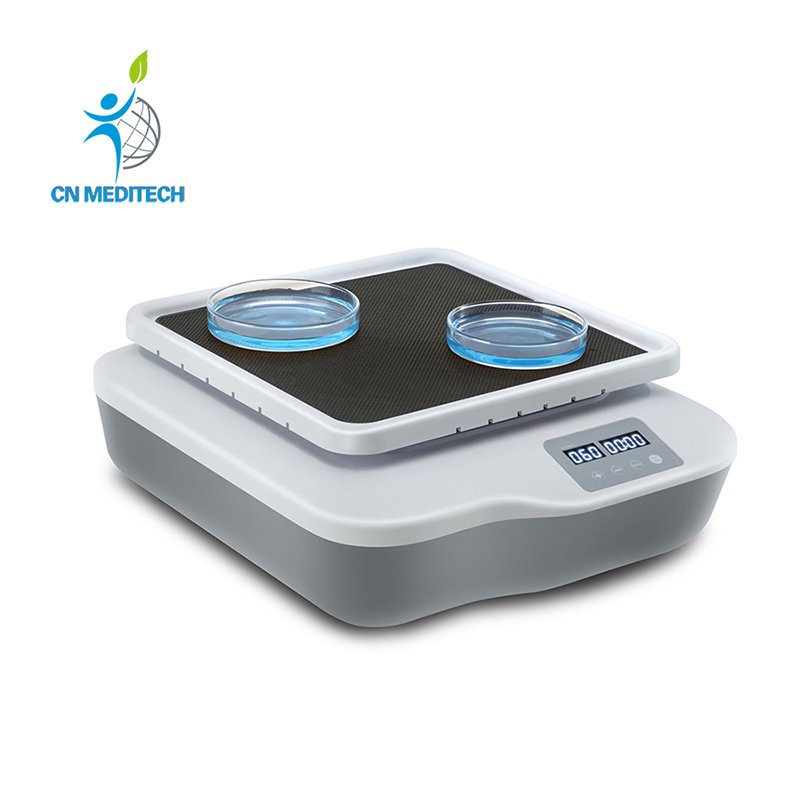
- Shaker: Offers linear, circular, or orbital shaking modes—widely used for promoting aerobic microbial growth (e.g., flask culture), reagent dissolution, or enhancing reaction mixing.
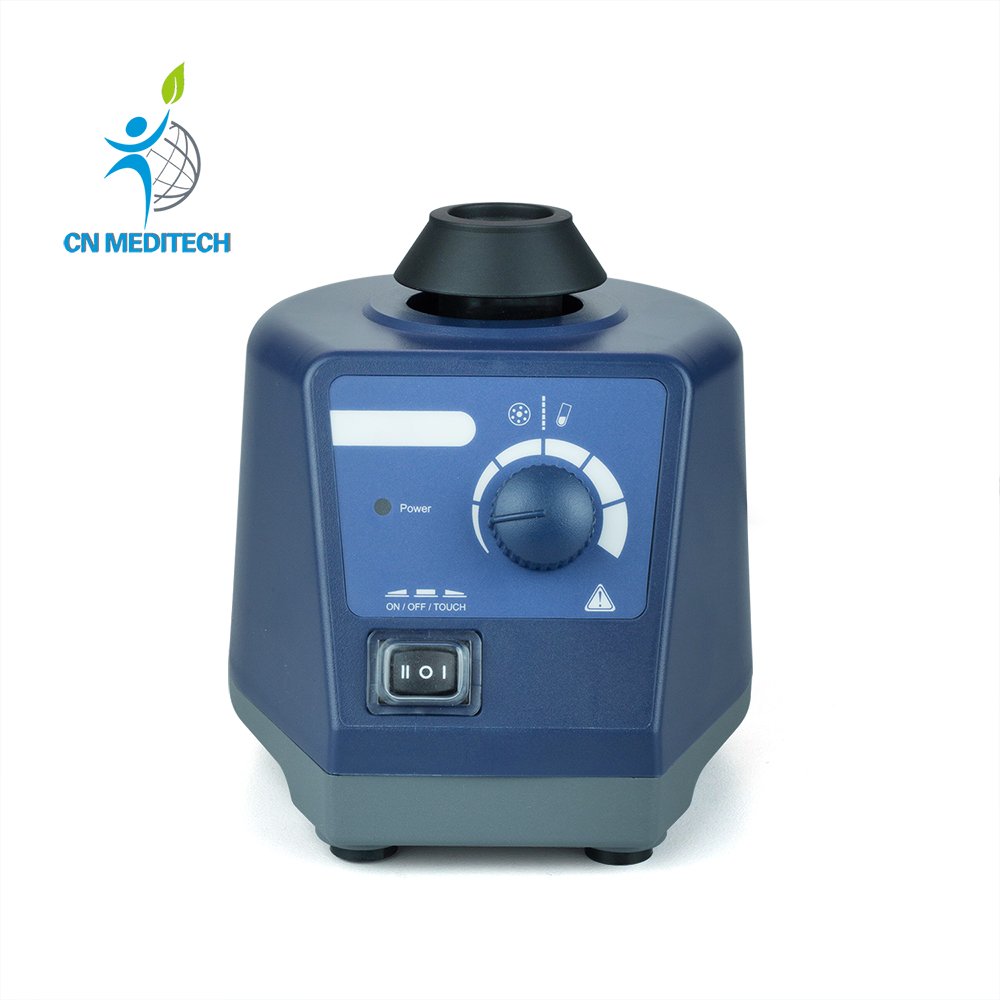
- Vortex Mixer:Uses oscillating or vortex motion for vigorous mixing to quickly resuspend precipitates, mix micro-volumes of liquids, or homogenize reaction systems.
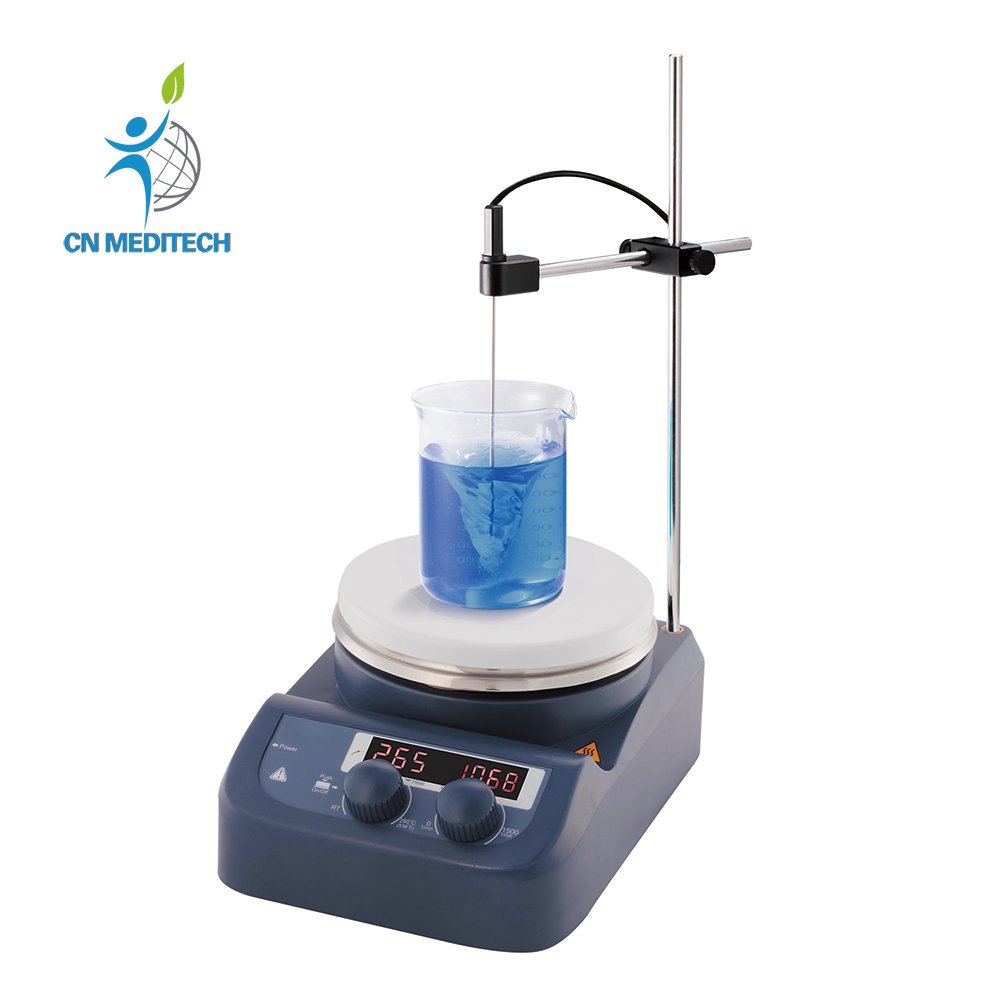
- Magnetic Stirrer: Drives a magnetic stir bar in a container via a rotating magnetic field to achieve gentle, continuous liquid mixing, dissolution, or heat-assisted mixing.
- Hotplates: Provides uniform heating through the surface of an electric plate for test tubes, beakers, and other vessels, suitable for all kinds of heating reaction steps.
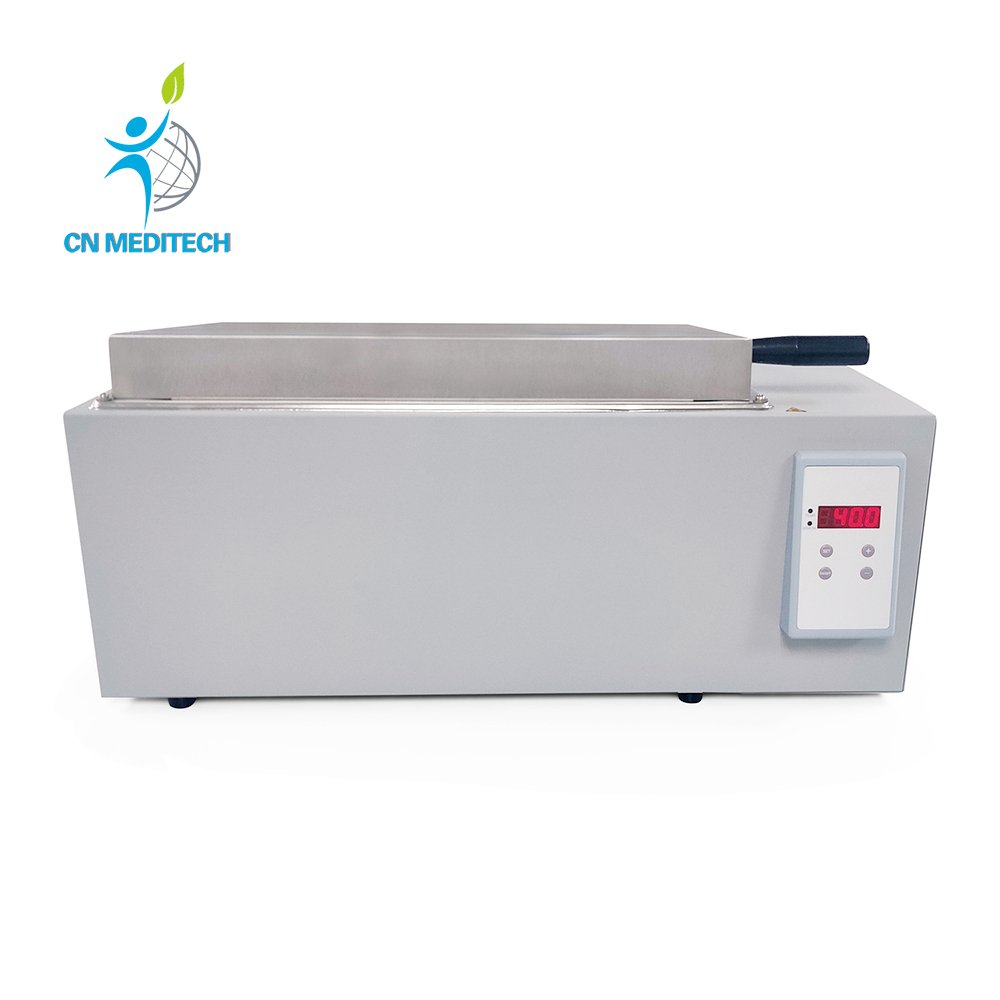
- Water Bath: Uses constant-temperature water to provide a precise and stable thermal environment—widely used in serum thawing, plasma inactivation, enzyme activity assays, and incubation.
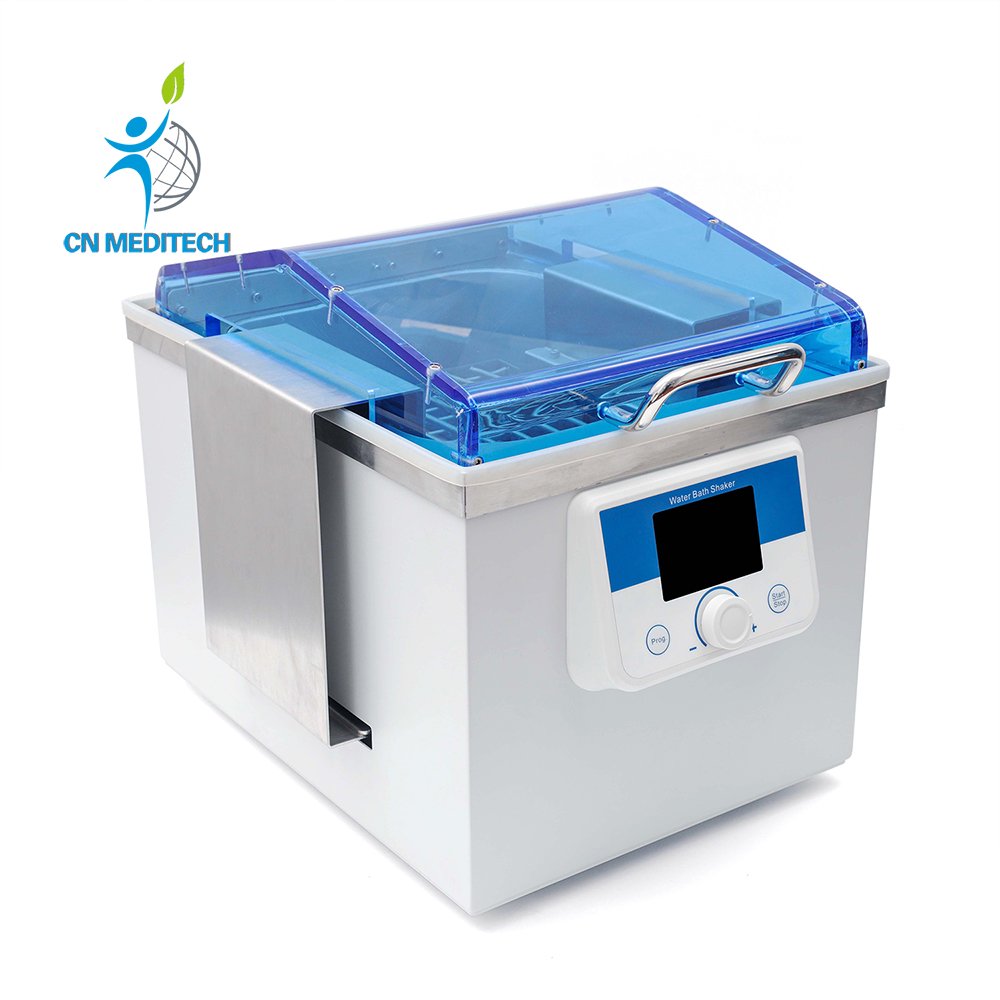
- Water BathShaker: Adds oscillation to the water bath function to accelerate dissolution and extraction processes, enhancing the uniformity of solution mixing and material exchange.

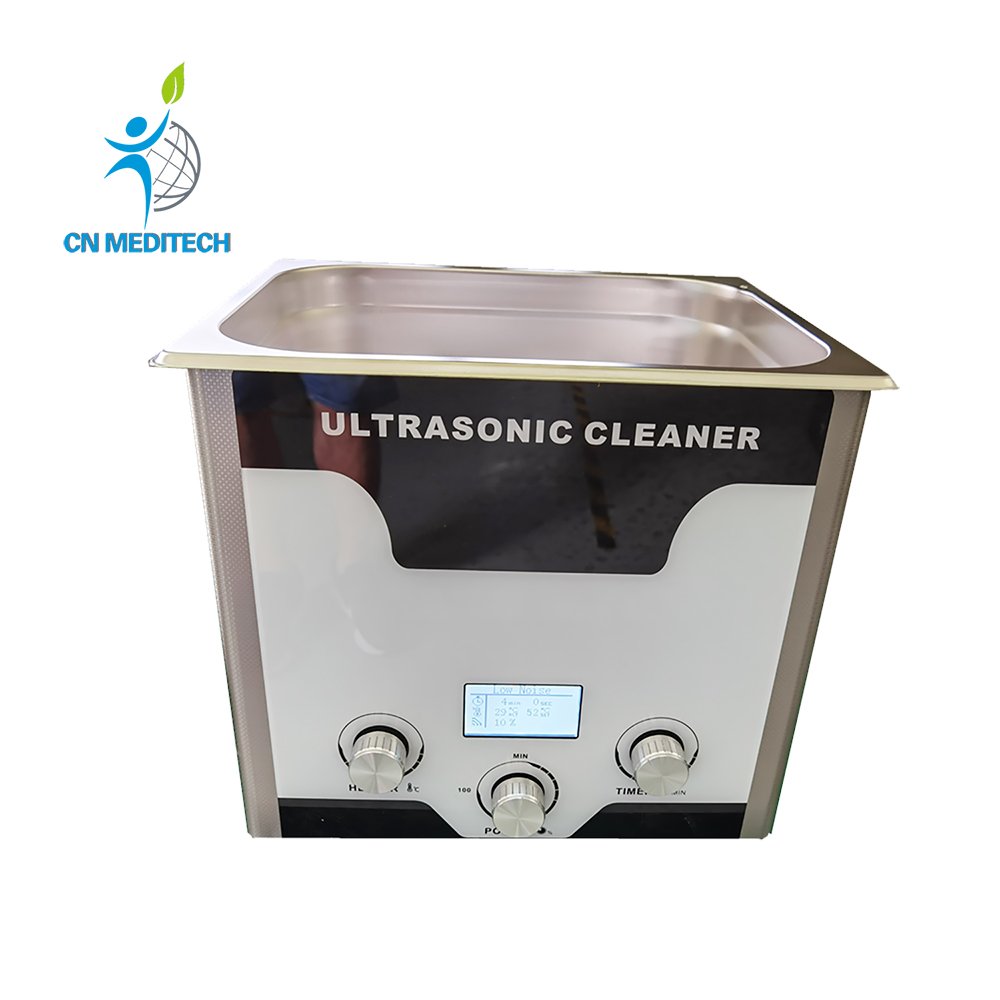
- Ultrasonic Cleaner: Uses high-frequency ultrasonic waves in liquid to powerfully and efficiently remove stubborn residues, grease, or particles from glassware and instrument parts—also applicable for cell suspension, tissue disruption, or emulsification.

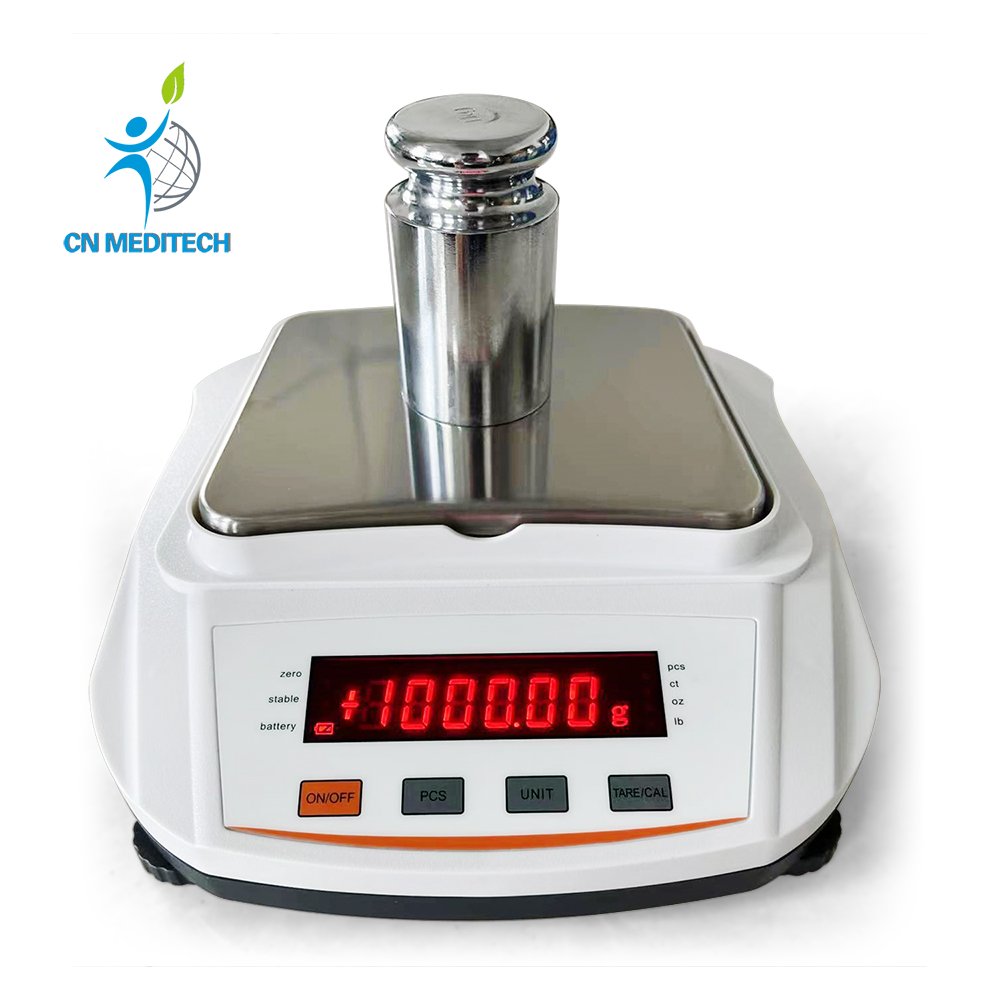
- Electronic Balance:High-precision weighing device for accurately measuring chemicals, drugs, biological samples, tissue slices, and preparation of standard solutions.
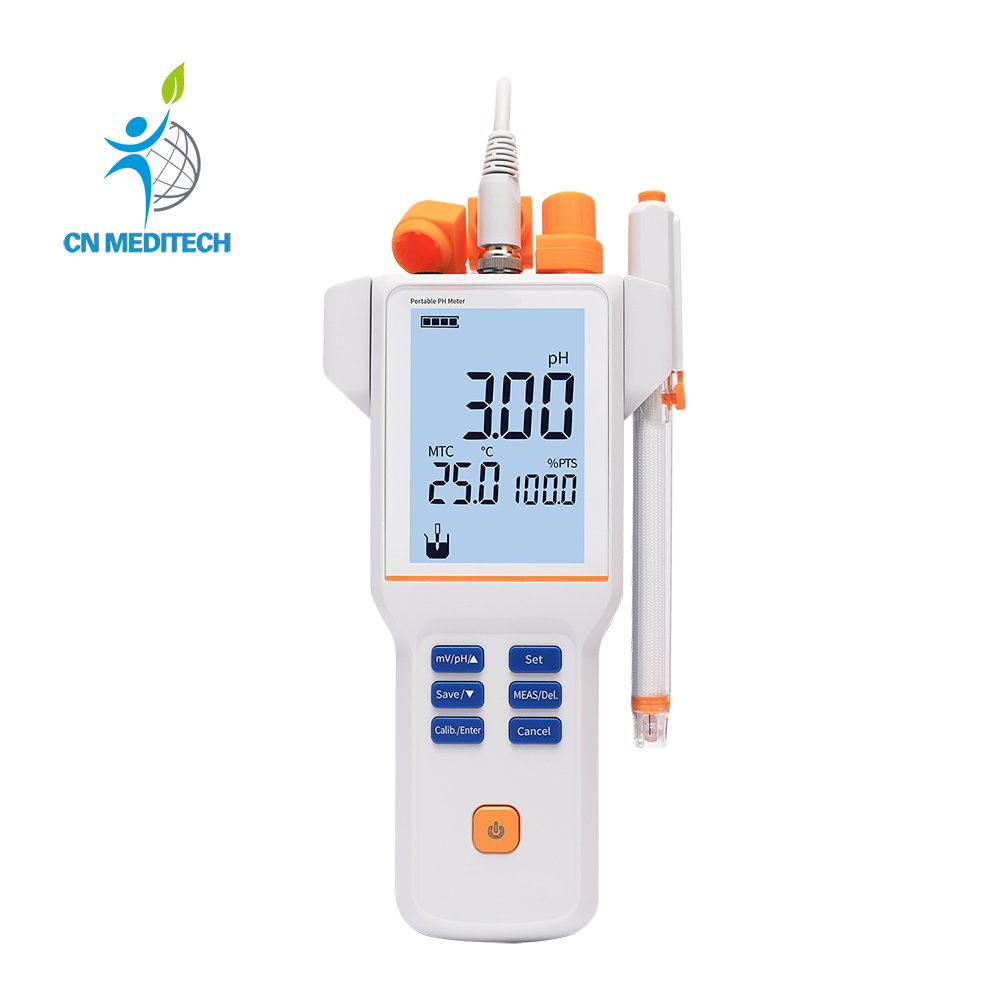
- PH Meter:Accurately measures the hydrogen ion concentration in aqueous solutions via a glass pH electrode—crucial for experimental condition control, solution calibration, and quality control.
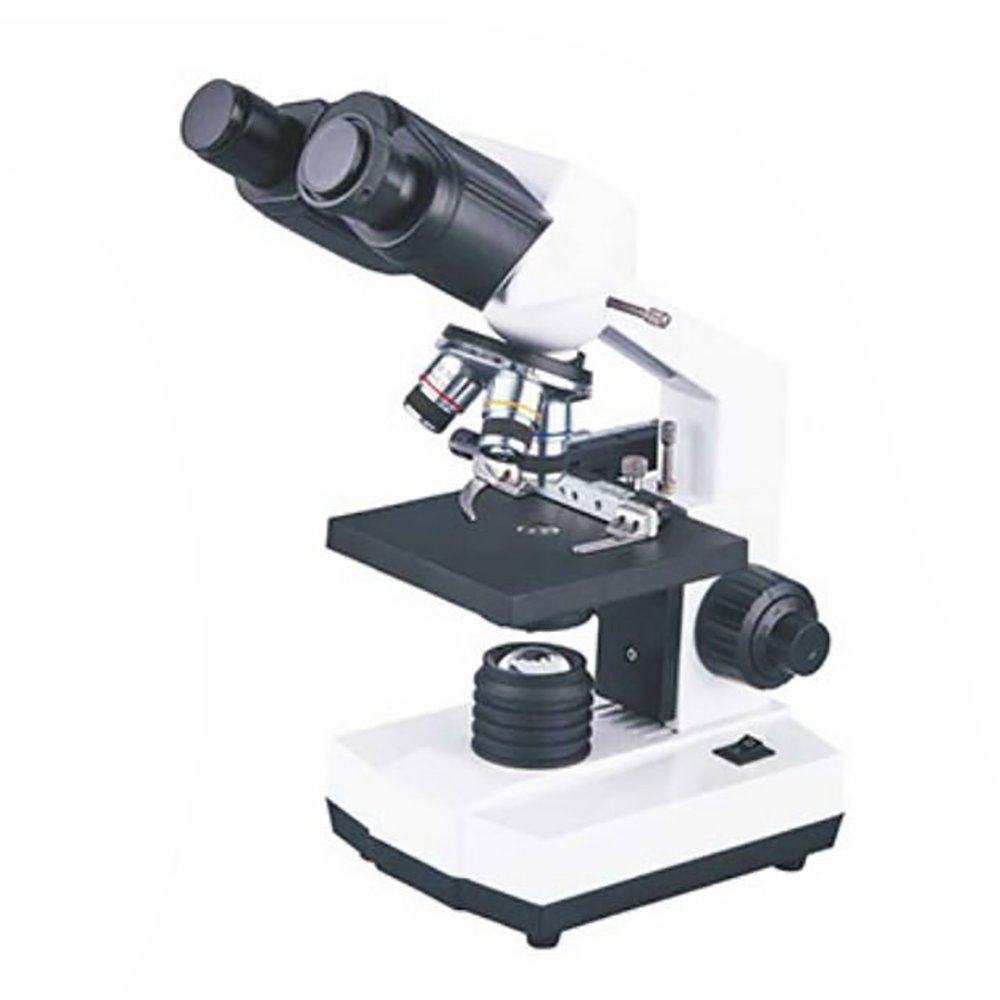
- Microscope:Includes brightfield microscopes, inverted microscopes (for culture observation), fluorescence microscopes (for immunofluorescence/FISH labeling), and phase contrast microscopes (for live cell observation). Essential tools for examining microscopic biological structures (bacteria, viruses, cell morphology, histological sections) and stained samples.
Other Laboratory Equipment
- Freezer Dryer:Freezes aqueous samples and removes water via sublimation under vacuum to preserve bacterial strains, viral vaccines, plasma derivatives, protein formulations, and enzymes for long-term stability.
- Electrophoresis:Applies an electric field to separate charged molecules in a gel matrix by size, charge, or conformation—commonly used in DNA/protein purity analysis, agarose/PAGE gel separation, and sequencing.
- Spectrophotometer: Measures absorbance of solutions at specific wavelengths—used for rapid quantitative analysis of nucleic acids, proteins, and cell concentrations.
- WaterDistiller: Produces highly purified deionized water through steam condensation, meeting stringent requirements for low-ion content in lab-grade water.
- Glassware Washer: Fully automated system for high-quality washing, rinsing, high-temperature flushing, and drying of laboratory glassware such as bottles, test tubes, and pipettes—ensuring cleanliness and sterility.
- Platelet Agitator: Simulates in vivo blood circulation by providing gentle linear horizontal agitation at 37°C to prevent platelet clumping, sedimentation, and functional loss—ensuring transfusion efficacy.
- Automatic PMCC Flash Point Tester: Highly integrated device for liquid handling, incubation, reaction, detection, and data analysis—enabling high-throughput, efficient, and standardized testing for multiple clinical items.
- Medical Drying Cabinet: Provides dehumidified or controlled humidity-temperature environments for safe storage of moisture-sensitive items such as reagents, enzymes, antibodies, dry powder media, electronic components, and analytical sensors.
- Blood Tube Sealer: Seals disposable blood specimen tubes or blood bag tubing by heat pressing to ensure safe sample transport and prevent biohazard leakage.
- Sterile Tube Welder: Uses high-frequency heating to aseptically weld multiple blood bags’ tubing—essential for ensuring sterile connections in blood centers and transfusion labs.
- Chlorine Tester:Accurately monitors residual hypochlorite or chlorine gas in water treatment systems to ensure proper disinfection without excessive corrosion or toxicity.
- Needle Destroyer: Instantly melts and destroys needle hubs or deforms the metal part of used needles and lancets to prevent injury or cross-infection with bloodborne pathogens.
- Ice Maker: Continuously produces crushed or cube ice for rapid cooling or reaction termination, temporary storage/transport of samples and reagents, or physical cooling applications—an essential laboratory support facility.
Selecting Suitable Medical Lab Equipment Suppliers
- Quality and Reliability:Evaluate manufacturing processes, material quality, and product lifespan. Key goals include durability and low failure rates, which are essential for operational continuity and data accuracy.
- Technical Support and Service:Assess the supplier’s response time, professional maintenance capabilities, and spare parts availability. Efficient technical support is crucial for quickly resolving issues and minimizing downtime.
- Innovation and Technology:Focus on suppliers with cutting-edge technologies and continuous R&D investment. Innovative suppliers better support laboratories in facing future research challenges.
- Customization and Flexibility:Confirm the supplier’s ability to offer tailored solutions—functional integration, interface expansion, or custom development for special applications to meet unique lab processes and research needs.
Conclusion
The precision, reliability, and multifunctionality of medical laboratory equipment are critical for improving diagnostic accuracy, optimizing lab efficiency, ensuring personnel safety, and advancing scientific research. Choosing the right supplier directly impacts a laboratory’s long-term operational capacity and research level.
As a professional supplier of medical laboratory equipment, CN MEDITECH focuses on integrating global leading technologies. With a rigorous quality evaluation system, efficient localized technical support and spare parts supply, and continuous access to innovative resources, we provide tailored solutions for all types of laboratories. We understand and prioritize customized services and are equipped to flexibly respond to the specific processes and unique application needs of different laboratories.











